Beginning with Financial metrics for startups, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
Financial metrics play a crucial role in the success of startups, providing valuable insights into their financial health and performance. By tracking key metrics and performance indicators, startups can make informed decisions that drive growth and sustainability. This guide explores the importance of financial metrics, different types of metrics, key performance indicators, and financial ratio analysis specifically tailored for startups.
Importance of Financial Metrics for Startups
Financial metrics play a crucial role in the success of startups by providing valuable insights into the financial health and performance of the business. Tracking key financial metrics allows startups to make informed decisions, identify areas of improvement, and measure progress towards their goals.
Examples of Key Financial Metrics
- Revenue Growth Rate: This metric measures the rate at which a startup’s revenue is increasing over a specific period. A healthy revenue growth rate indicates that the business is on a growth trajectory.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC helps startups understand how much it costs to acquire a new customer. By tracking this metric, startups can optimize their marketing strategies and improve profitability.
- Runway: Runway is the amount of time a startup can operate before running out of funds. It is essential for startups to monitor their runway to ensure they have enough capital to sustain operations and reach key milestones.
- Profit Margin: Profit margin indicates the percentage of revenue that translates into profit. Startups need to track their profit margin to ensure they are generating enough profit to support growth and sustainability.
How Financial Metrics Help Startups Make Informed Decisions
Financial metrics provide startups with quantifiable data that can guide decision-making processes. By analyzing key financial metrics, startups can:
- Identify areas of inefficiency and implement cost-saving measures.
- Evaluate the success of marketing campaigns and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Set realistic financial goals and track progress towards achieving them.
- Make informed investment decisions based on financial performance and projections.
Types of Financial Metrics
Financial metrics are crucial for startups to track and analyze their financial performance. There are various categories of financial metrics that provide valuable insights into different aspects of a startup’s financial health.
Revenue Metrics
Revenue metrics focus on the income generated by the startup through its products or services. These metrics help in assessing the effectiveness of the revenue generation strategies and the overall growth of the business. Examples of revenue metrics include:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): A key metric for subscription-based startups, MRR helps in predicting future revenue and assessing the stability of cash flow.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): This metric calculates the total revenue a startup can expect from a single customer over their entire relationship with the company, helping in customer acquisition and retention strategies.
Expenses Metrics
Expenses metrics track the costs incurred by the startup in running its operations. Monitoring these metrics is essential to ensure efficient resource allocation and cost management. Examples of expenses metrics include:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric calculates the average cost of acquiring a new customer, helping in evaluating the effectiveness of marketing and sales efforts.
- Operating Expenses Ratio: This metric compares the operating expenses of the startup with its revenue, indicating the efficiency of cost control and operational management.
Cash Flow Metrics
Cash flow metrics focus on the movement of cash in and out of the startup, providing insights into its liquidity and financial stability. Examples of cash flow metrics include:
- Operating Cash Flow: This metric measures the cash generated from the core operations of the startup, indicating its ability to cover day-to-day expenses.
- Cash Runway: This metric calculates the time period a startup can sustain its operations with the available cash, helping in strategic financial planning and fundraising decisions.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Startups
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. They are essential for measuring startup performance as they provide a clear picture of progress towards goals and help in identifying areas that need improvement.
Definition and Importance of KPIs
KPIs differ from other financial metrics in that they are specifically tailored to the unique goals and objectives of a startup. While financial metrics focus on the overall financial health of a company, KPIs are more targeted and can vary depending on the industry, business model, and stage of the startup.
Examples of Common KPIs for Startups
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This KPI measures how much it costs to acquire a new customer and helps startups understand the effectiveness of their marketing and sales efforts.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): MRR is a key indicator of a startup’s growth and stability, as it represents the predictable revenue stream from subscription-based customers.
- Churn Rate: Churn rate measures the percentage of customers who stop using a product or service over a given period, indicating customer satisfaction and retention.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV helps startups understand the long-term value of a customer and guides decisions on marketing investments and customer acquisition strategies.
These KPIs are crucial for startups as they provide insights into customer acquisition, revenue generation, customer retention, and overall business performance, enabling founders and investors to make informed decisions and drive growth.
Financial Ratio Analysis for Startups
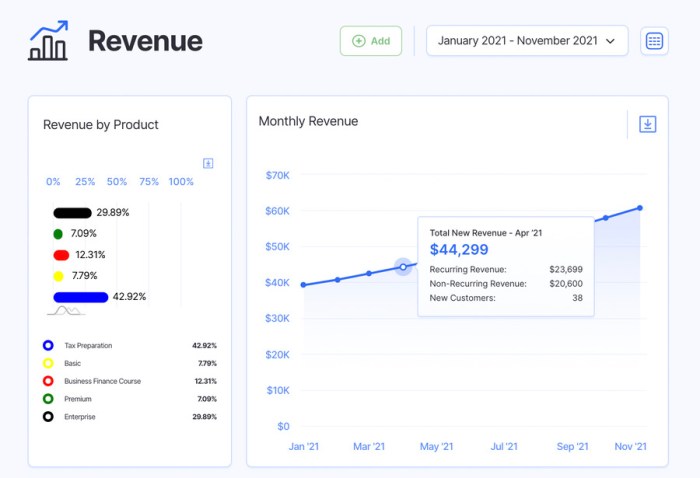
Financial ratio analysis is a crucial tool for evaluating a startup’s financial health as it provides insights into various aspects of the business’s performance. By examining different ratios, stakeholders can assess the company’s liquidity, profitability, efficiency, and overall financial stability.
Key Financial Ratios for Startups
- Liquidity Ratios: Liquidity ratios measure a startup’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. The most common liquidity ratios include the current ratio and the quick ratio. A current ratio above 1 indicates that the company can cover its short-term liabilities with its current assets.
- Profitability Ratios: Profitability ratios help determine how effectively a startup is generating profit. Key profitability ratios include gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on equity. These ratios reflect the company’s ability to generate income relative to its expenses and investments.
- Efficiency Ratios: Efficiency ratios assess how well a startup utilizes its resources to generate revenue. Examples of efficiency ratios are asset turnover ratio and inventory turnover ratio. A high asset turnover ratio indicates that the company is effectively using its assets to generate sales.
Interpreting Financial Ratios
Financial ratios provide valuable insights into a startup’s financial performance. For instance, a high current ratio may indicate that the company has excess cash that could be reinvested in the business. On the other hand, a declining gross profit margin may signal inefficiencies in production or pricing strategies. It is essential to compare these ratios with industry benchmarks to gain a better understanding of the startup’s financial standing.
