Delving into high-dividend yield stocks, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a focus on the financial opportunities and risks associated with these investments. Understanding the intricacies of high-dividend yield stocks is essential for investors looking to maximize their returns in the stock market.
In this guide, we will explore the definition of high-dividend yield stocks, their benefits, risks, and strategies for selecting the right stocks to build a diversified portfolio. By the end of this discussion, readers will have a deeper insight into the world of high-dividend yield stocks and how they can play a crucial role in an investment portfolio.
What are High-Dividend Yield Stocks?
High-dividend yield stocks are stocks of companies that pay out a relatively high dividend compared to their stock price. These stocks are sought after by investors looking for regular income in the form of dividends.
Dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the price per share. It is expressed as a percentage and indicates the return on investment from dividends alone.
Examples of Industries with High-Dividend Yield Stocks
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): REITs are known for their high dividend yields due to their obligation to distribute a significant portion of their income to shareholders.
- Utilities: Companies in the utility sector often offer stable earnings and cash flows, allowing them to pay attractive dividends.
- Telecommunication: Telecommunication companies are known for their consistent cash flows, leading to high dividend payouts.
- Consumer Staples: Companies that produce essential goods like food, beverages, and household products tend to offer high dividend yields.
Benefits of Investing in High-Dividend Yield Stocks
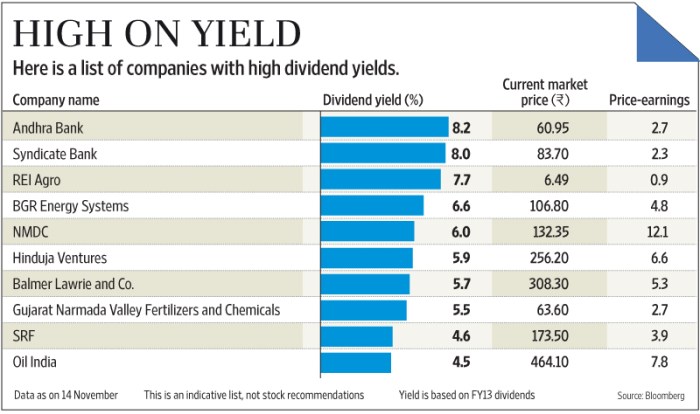
Investing in high-dividend yield stocks can offer several advantages to investors. These stocks are known for providing a consistent income stream through regular dividend payments. Additionally, high-dividend yield stocks can serve as a hedge against market volatility, helping investors navigate uncertain market conditions.
Steady Income Stream
High-dividend yield stocks are valued for their ability to generate a steady income stream for investors. Companies that pay out high dividends typically have a track record of stable earnings and cash flow. By investing in these stocks, individuals can rely on regular dividend payments, which can be particularly beneficial for those seeking a consistent source of income, such as retirees.
Hedge Against Market Volatility
Another key benefit of investing in high-dividend yield stocks is their potential to offer a hedge against market volatility. During times of market turbulence or economic downturns, dividend-paying stocks tend to be more resilient compared to non-dividend-paying stocks. This resilience can help cushion a portfolio from significant losses and provide a source of stability when other investments may be underperforming.
Risks Associated with High-Dividend Yield Stocks
Investing in high-dividend yield stocks can offer attractive returns, but it is important to acknowledge the risks involved. These risks can impact the performance of your investment and should be carefully considered before making investment decisions.
Economic Conditions and High-Dividend Yield Stocks
Economic conditions play a crucial role in the performance of high-dividend yield stocks. During economic downturns or recessions, companies may struggle to maintain their dividend payments, leading to potential cuts or suspensions. This can result in a decline in the stock price and diminished returns for investors. It is essential to monitor the overall economic health and stability of the market when investing in high-dividend yield stocks.
Impact of Changes in Interest Rates on High-Dividend Yield Stocks
Changes in interest rates can also have a significant impact on high-dividend yield stocks. When interest rates rise, fixed-income investments become more appealing to investors, potentially causing a shift away from dividend-paying stocks. This could lead to a decrease in demand for high-dividend yield stocks, resulting in a decrease in stock prices. Conversely, when interest rates are low, high-dividend yield stocks may become more attractive as investors seek higher yields. It is important to consider the prevailing interest rate environment when investing in high-dividend yield stocks to assess the potential impact on your investment portfolio.
Strategies for Selecting High-Dividend Yield Stocks
When looking to invest in high-dividend yield stocks, it is crucial to have a solid strategy in place. Here are some tips on how to evaluate and select the right high-dividend yield stocks for your portfolio.
Importance of Considering the Company’s Financial Health
It is essential to assess the financial health of a company before investing in its high-dividend yield stocks. A company with a strong balance sheet, positive cash flow, and steady earnings growth is more likely to sustain its dividends over the long term. Look for companies with low debt levels and a history of consistent dividend payments.
Significance of Dividend Payout Ratio
The dividend payout ratio is a key metric to consider when evaluating high-dividend yield stocks. This ratio indicates the percentage of earnings that a company pays out in dividends to its shareholders. A lower dividend payout ratio signifies that the company has more room to grow its dividends in the future. On the other hand, a high payout ratio may indicate that the company is using most of its earnings to pay dividends, leaving little room for reinvestment in the business.
- Ensure the dividend payout ratio is sustainable: A sustainable dividend payout ratio typically falls between 40% to 60% of a company’s earnings. This range allows the company to retain enough earnings for future growth while still rewarding shareholders with dividends.
- Compare the dividend payout ratio across different companies: When comparing high-dividend yield stocks, look for companies with lower payout ratios relative to their industry peers. This can indicate a more conservative approach to dividend payments and lower risk of dividend cuts in the future.
- Monitor changes in the dividend payout ratio over time: A consistent increase in the dividend payout ratio may signal financial distress or an unsustainable dividend policy. Regularly review this metric to ensure the company’s ability to maintain its dividend payments.
