Exploring the concept of leveraging debt, this guide delves into the strategies and risks associated with utilizing debt as a financial tool. From understanding debt leverage to practical examples of successful leveraging strategies, this article aims to provide a thorough insight into the topic.
As we navigate through the intricacies of debt leveraging, we will uncover the various types of debt, optimal strategies, and ways to mitigate risks in the process.
Understanding Debt Leverage
Debt leverage, in financial terms, refers to the strategy of using borrowed funds to increase the potential return on investment. It involves borrowing money to invest in projects or assets with the goal of generating higher returns than the cost of borrowing.
How Debt Leverage Can Be a Tool for Businesses
Debt leverage can be a valuable tool for businesses looking to expand or grow their operations. By using debt to finance investments, businesses can take advantage of opportunities that would not be possible with only equity financing. This allows companies to accelerate their growth and increase their profitability.
- Increased Returns: Debt leverage allows businesses to amplify their returns on investment. By using borrowed funds to finance projects, businesses can potentially earn higher returns than if they had used only their own capital.
- Financial Flexibility: Debt leverage provides businesses with the flexibility to pursue growth opportunities that may require a significant amount of capital. By leveraging debt, companies can access the funds needed to expand their operations or enter new markets.
- Tax Benefits: Interest payments on debt are often tax-deductible, which can reduce the overall tax burden for businesses. This tax advantage can make debt financing a more cost-effective option compared to equity financing.
Risks Associated with Using Debt Leverage
Using debt leverage also comes with certain risks that businesses need to consider before taking on additional debt.
- Increased Risk of Bankruptcy: Taking on too much debt can increase the risk of bankruptcy, especially if the business is unable to generate enough cash flow to meet its debt obligations.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can impact the cost of debt financing for businesses. Rising interest rates can lead to higher borrowing costs, which can affect profitability.
- Loss of Control: When a business takes on debt, it incurs an obligation to repay the borrowed funds. This can limit the company’s flexibility and control over its operations, as debt holders may impose certain restrictions or conditions on the business.
Types of Debt for Leveraging
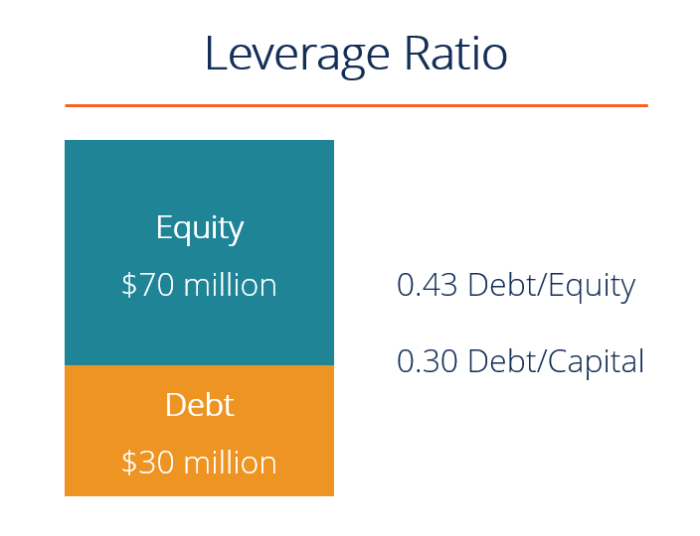
Debt leveraging involves using borrowed funds to invest in assets or projects with the goal of generating higher returns than the cost of borrowing. Different types of debt can be utilized for leveraging, each with its own unique characteristics and implications.
Short-Term Debt
Short-term debt typically has a maturity period of less than one year and is often used for working capital needs or to finance inventory. While short-term debt can provide quick access to funds, it usually comes with higher interest rates compared to long-term debt. This type of debt can be beneficial for leveraging in situations where the investment horizon is short-term and the returns are expected to be realized quickly.
Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt, on the other hand, has a maturity period exceeding one year and is commonly used for financing large capital expenditures or real estate purchases. Long-term debt generally offers lower interest rates than short-term debt, making it a more cost-effective option for leveraging over extended periods. Leveraging with long-term debt is suitable for investments with a longer time horizon, where the returns may take time to materialize.
Interest Rates in Debt Leveraging
Interest rates play a crucial role in debt leveraging strategies as they directly impact the cost of borrowing and the overall profitability of investments. Lower interest rates can enhance the leverage effect by reducing borrowing costs and increasing potential returns. Conversely, high interest rates can erode profits and increase the risk of leveraging, especially if the returns on investments do not exceed the cost of debt. It is essential for investors to carefully consider interest rate trends and choose the most suitable type of debt for leveraging based on their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Strategies for Leveraging Debt
When it comes to leveraging debt, it is crucial to have a well-thought-out strategy in place. This involves determining the optimal level of debt for leveraging, looking at successful real-world examples, and maintaining a balance between equity and debt.
Steps to Determine the Optimal Level of Debt for Leveraging
Before deciding on the amount of debt to leverage, it is essential to assess your financial situation thoroughly. Here are some key steps to determine the optimal level of debt:
- Evaluate your current financial position, including assets, income, and existing debt.
- Conduct a risk assessment to understand the potential implications of taking on more debt.
- Consider your future financial goals and how leveraging debt can help you achieve them.
- Analyze the cost of debt and compare it to the potential returns on investment.
- Consult with financial advisors or experts to get personalized advice based on your unique circumstances.
Examples of Successful Debt Leveraging Strategies in Real-World Scenarios
There are numerous examples of successful debt leveraging strategies in real-world scenarios, where companies and individuals have effectively utilized debt to grow their wealth or business. Some examples include:
- Real estate investors leveraging mortgages to purchase properties and generate rental income.
- Businesses using debt to finance expansion projects that result in increased revenue and profitability.
- Individuals investing in stocks using margin loans to amplify their returns in a rising market.
The Importance of Maintaining a Balance Between Equity and Debt When Leveraging
While leveraging debt can be a powerful tool for wealth creation, it is essential to maintain a balance between equity and debt to mitigate risks. By having a healthy mix of equity and debt in your portfolio, you can:
- Diversify your sources of funding and reduce dependence on a single type of financing.
- Lower the overall cost of capital by optimizing the use of debt and equity based on their respective costs.
- Manage financial leverage effectively to avoid overexposure to debt and potential financial distress.
Risks and Mitigation
Debt leverage can be a powerful tool for financial growth, but it also comes with inherent risks that need to be carefully managed to avoid potential negative consequences. Understanding these risks and knowing how to mitigate them is crucial for successful debt leveraging strategies.
Common Risks Associated with Leveraging Debt
- Interest Rate Risk: Fluctuations in interest rates can significantly impact the cost of debt, leading to higher payments and potentially affecting profitability.
- Market Risk: Changes in the market conditions, such as economic downturns or industry-specific challenges, can affect the ability to generate returns to cover debt obligations.
- Liquidity Risk: Using debt to finance investments may limit available cash flow for other operational needs, potentially leading to liquidity issues.
- Repayment Risk: Inability to meet debt repayment obligations can result in penalties, lower credit ratings, and even bankruptcy.
Ways to Mitigate Risks in Debt Leveraging
- Diversification: Spreading debt across different investments or asset classes can help reduce the impact of any single investment underperforming.
- Stress Testing: Conducting scenario analysis to assess how different market conditions would affect the ability to meet debt obligations can help in preparing for potential risks.
- Conservative LTV Ratios: Maintaining lower loan-to-value ratios can provide a buffer against unexpected declines in asset values.
- Reserve Funds: Setting aside funds for debt servicing and contingencies can help mitigate liquidity risks and ensure timely repayments.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Debt Leveraging Decisions
- Interest Rate Environment: High interest rates can increase the cost of debt and make leveraging less attractive, while low rates may encourage borrowing for investment.
- Economic Stability: A stable economic environment with predictable growth can provide confidence for leveraging debt, while economic uncertainties may lead to more conservative borrowing decisions.
- Industry Trends: Understanding industry-specific risks and opportunities is crucial in assessing the impact of economic conditions on debt leveraging strategies.
