Delving into Understanding mutual funds, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, providing a detailed explanation of mutual funds, how they work, different types, and the associated risks and rewards.
Exploring the intricacies of mutual funds opens up a world of investment opportunities that individuals can leverage for financial growth and stability.
What are mutual funds?
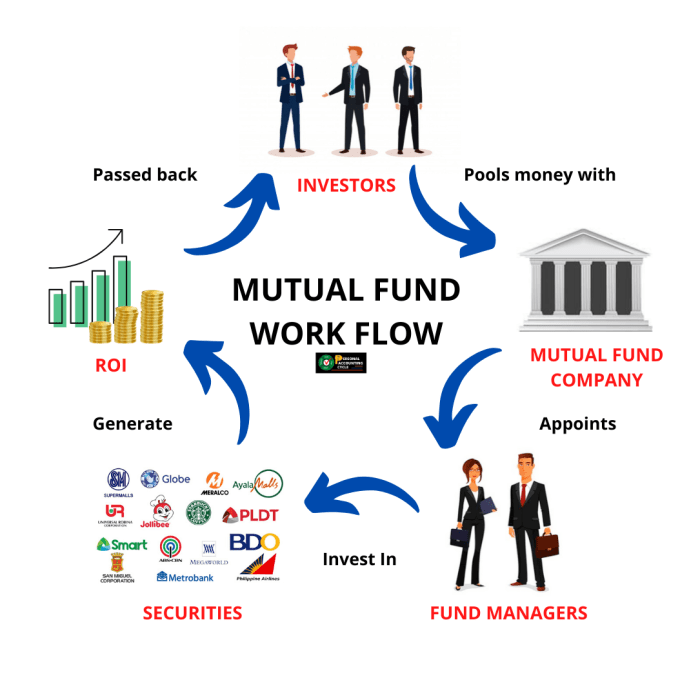
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
Types of mutual funds
- Equity Funds: These funds invest primarily in stocks, offering the potential for high returns but also higher risk.
- Bond Funds: These funds invest in fixed-income securities, providing regular income and lower risk compared to equity funds.
- Money Market Funds: These funds invest in short-term, low-risk securities such as Treasury bills and commercial paper, suitable for investors seeking stability and liquidity.
- Index Funds: These funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, at a lower cost compared to actively managed funds.
Benefits of investing in mutual funds
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer investors exposure to a wide range of securities, reducing individual investment risk.
- Professional Management: Fund managers conduct research and make investment decisions, saving investors time and effort.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds allow investors to buy and sell shares on any business day at the fund’s net asset value (NAV).
- Accessibility: Mutual funds have varying minimum investment requirements, making them accessible to a wide range of investors.
How do mutual funds work?
When investors purchase shares of a mutual fund, they are pooling their money with other investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
Investing in mutual funds
- Investors can buy shares of a mutual fund directly from the fund company or through a broker.
- Investors can choose from different types of mutual funds based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Investors can invest a specific amount of money or set up automatic investments to regularly contribute to the fund.
Role of fund managers
- Fund managers are responsible for selecting the securities that make up the fund’s portfolio.
- They conduct research, analyze market trends, and make buy/sell decisions to achieve the fund’s investment objectives.
- Fund managers monitor the performance of the fund and make adjustments to the portfolio as needed.
Generating returns for investors
- Mutual funds generate returns for investors through dividends, interest income, and capital gains from the securities in the portfolio.
- Investors can earn returns when the value of the securities in the fund’s portfolio increases.
- Some mutual funds also distribute income and capital gains to investors in the form of dividends.
Types of mutual funds.
Mutual funds can be broadly categorized into three main types: equity funds, debt funds, and hybrid funds. Each type of fund has its own unique characteristics and level of risk associated with it.
Equity Mutual Funds
Equity mutual funds primarily invest in stocks or shares of companies. These funds offer the potential for high returns but also come with a higher level of risk due to the volatility of the stock market. Examples of popular equity mutual funds include:
- Large Cap Funds: Invest in large, well-established companies with a track record of stable performance. Example: HDFC Top 100 Fund.
- Mid Cap Funds: Invest in mid-sized companies with the potential for growth. Example: ICICI Prudential Midcap Fund.
- Small Cap Funds: Invest in small companies with high growth potential. Example: SBI Small Cap Fund.
Debt Mutual Funds
Debt mutual funds primarily invest in fixed-income securities such as government bonds, corporate bonds, and other debt instruments. These funds offer lower returns compared to equity funds but are considered less risky. Examples of popular debt mutual funds include:
- Short-Term Debt Funds: Invest in securities with short maturity periods, resulting in lower interest rate risk. Example: Axis Short Term Fund.
- Long-Term Debt Funds: Invest in securities with longer maturity periods, offering higher returns but with higher interest rate risk. Example: Franklin India Income Opportunities Fund.
Hybrid Mutual Funds
Hybrid mutual funds, also known as balanced funds, invest in a mix of equities and debt instruments to provide a balanced portfolio. These funds aim to offer the benefits of both asset classes while minimizing overall risk. Examples of popular hybrid mutual funds include:
- Aggressive Hybrid Funds: Invest a higher proportion in equities for growth potential. Example: Mirae Asset Hybrid Equity Fund.
- Conservative Hybrid Funds: Invest a higher proportion in debt for stability. Example: Aditya Birla Sun Life Regular Savings Fund.
How to choose a mutual fund?
When selecting a mutual fund, there are several factors to consider to make an informed decision. It is essential to analyze the past performance of the fund, understand its objectives, and diversify investments effectively.
Factors to consider when selecting a mutual fund
- Expense Ratio: Look for funds with lower expense ratios as they can significantly impact your returns over time.
- Risk Tolerance: Consider your risk tolerance level and choose a fund that aligns with your investment goals.
- Investment Goals: Evaluate whether the fund’s objectives match your financial objectives and time horizon.
- Historical Performance: Analyze the fund’s past performance to assess its consistency and returns over different market conditions.
Importance of analyzing past performance and fund objectives
Analyzing a mutual fund’s past performance can provide insights into how the fund has weathered various market conditions and whether it has met its objectives. Understanding the fund’s objectives is crucial to ensure that it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Tips for diversifying investments through mutual funds
- Asset Allocation: Spread your investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to reduce risk.
- Choose Different Fund Types: Invest in a mix of mutual funds, including equity funds, bond funds, and index funds, to diversify your portfolio.
- Rebalance Regularly: Monitor your investments periodically and rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation.
Understanding mutual fund fees.
When investing in mutual funds, it is crucial to understand the various fees associated with these investments. Fees can significantly impact your investment returns over time, so it is essential to be aware of them and take steps to minimize expenses.
Types of Mutual Fund Fees
- Management Fees: These fees are paid to the fund manager for managing the fund’s investments. They are typically charged as a percentage of the fund’s assets.
- Expense Ratios: This ratio represents the percentage of the fund’s assets that are used to cover operating expenses. It includes management fees, administrative costs, and other expenses.
- Load Fees: Load fees are sales charges that investors may pay when buying or selling mutual fund shares. There are front-end loads (paid when purchasing shares) and back-end loads (paid when selling shares).
- Transaction Fees: These fees are charged when investors buy or sell shares of a mutual fund. They are not part of the expense ratio but can impact overall returns.
Impact of Fees on Investment Returns
The impact of fees on investment returns can be significant over the long term. Even seemingly small differences in fees can add up and erode your returns. For example, a mutual fund with a 1% expense ratio will eat into your returns more than a fund with a 0.5% expense ratio, assuming all other factors are equal.
It’s essential to consider fees when evaluating mutual fund options, as they can have a substantial impact on your overall investment performance.
Strategies to Minimize Mutual Fund Expenses
- Look for low-cost index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds.
- Avoid funds with high sales loads, as these charges can reduce your initial investment amount and erode returns over time.
- Consider investing in no-load funds that do not charge sales commissions, allowing you to invest the full amount without deductions.
- Regularly review and compare expense ratios of different mutual funds to ensure you are minimizing costs while achieving your investment goals.
Risks and rewards of investing in mutual funds.
When investing in mutual funds, it is important to consider both the risks and rewards associated with this type of investment. Understanding these aspects can help investors make informed decisions and manage their portfolios effectively.
Investing in mutual funds comes with certain risks that investors should be aware of. Some of the key risks involved in mutual fund investments include market risk, liquidity risk, credit risk, and interest rate risk. Market risk refers to the possibility of losing money due to fluctuations in the overall market. Liquidity risk is the risk of not being able to sell your investment quickly without impacting the price. Credit risk refers to the risk of the issuer defaulting on their payments. Interest rate risk is the risk of losing money due to changes in interest rates.
On the other hand, there are potential rewards and benefits of investing in mutual funds. These include diversification, professional management, liquidity, convenience, and the potential for higher returns compared to other investment options. Diversification helps spread risk across different assets, reducing the impact of a single investment’s poor performance. Professional management ensures that experienced fund managers are making investment decisions on behalf of investors. Liquidity allows investors to buy and sell mutual fund shares easily. Convenience comes from the ease of investing in mutual funds through online platforms or financial advisors. Lastly, mutual funds have the potential for higher returns over the long term compared to individual stock picking.
To manage risks while investing in mutual funds, investors can employ various strategies. These include diversifying their investments across different asset classes, regularly reviewing and rebalancing their portfolios, understanding their risk tolerance, investing for the long term, and staying informed about market trends and economic indicators. By following these strategies, investors can mitigate risks and increase their chances of achieving their financial goals through mutual fund investments.
